MA3304 Methods of Applied Mathematics 2020/21
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
2020/21
MA3304
Methods of Applied Mathematics
Formulae
Power series
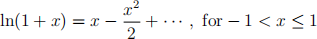
Definite integral
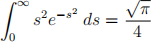
Perturbation Expansions
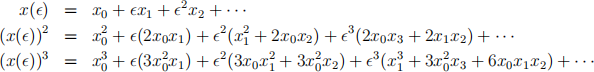
Trigonometric Identities
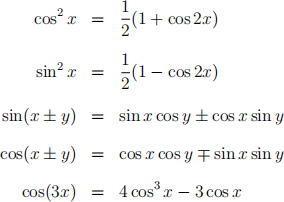
1. (a) Show that one of the roots of the equation
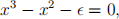
where  > 0 is a small parameter is given by
> 0 is a small parameter is given by
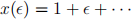
Determine the leading two terms in the asymptotic expansions of the other two roots.
(b) Find the first three terms in the expansion
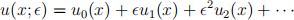
of the solution of the differential equation
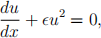
where u(0) = 1 and 0 <  << 1.
<< 1.
(c) Solve the Fredholm integral equation
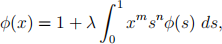
where m and n are non-negative integers and find the eigenvalues of the associated
homogeneous equation.
(d) Reformulate the following boundary value problem
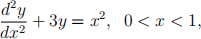
with y(0) = 1, y'(1) = 0, as an equivalent integral equation in the form
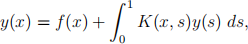
where f (x) and K(x, s) should be specified.
(e) Consider the problem of minimising the functional
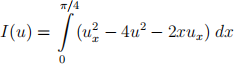
in the set of admissible functions
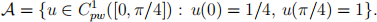
Write down the Euler-Lagrange equation and determine the only solution u to this equation in the set A.
2. (a) Use Laplace’s method to obtain the leading term in the asymptotic expansion as x → o of the following integral
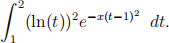
Provide justifications for any approximations that you use to derive the result. [10] (b) Consider the following initial value problem
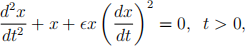
where 0 <  < 1 is a small parameter with
< 1 is a small parameter with
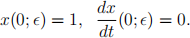
Use the Poincar´e-Linstedt method to show that a uniformly valid expansion of the solution to this problem is given by
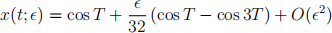
where 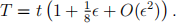
3. (a) Consider the Fredholm integral equation
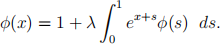
i. Use the method of successive approximations to generate a Neumann series approximation to this equation that is valid for |λ| < A where A needs to be determined.
ii. Calculate the first three iterated kernels and determine an expression for the resolvent kernel. Hence derive a closed from expression for the solution of the equation.
(b) Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the integral equation
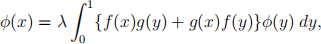
where f (x) and g(x) are real-valued continuous functions satisfying
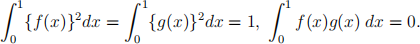
With reference to these integral properties, explain why f (x) and g(x) are linearly independent.
4. Consider the problem of minimising the functional:
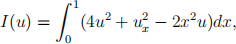
over the set of admissible functions
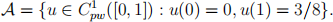
(a) Write down the weak Euler-Lagrange equation for the minimisation problem as- sociated with the functional.
(b) Find the solution for the corresponding Euler-Lagrange equation.
(c) Write the second variation of the functional.
(d) Explain why the solution of the Euler-Lagrange equation obtained in part (b) of the question is a weak local minimiser by solving the corresponding Jacobi equation. Refer to any relevant theorems that you use.
(e) Find the solution of the Euler-Lagrange equation from part (b) of the question if the set of admissible functions is replaced by
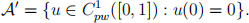
2022-01-14