MATH11153 Discrete-Time Finance
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Discrete-Time Finance
MATH11153
(1) Consider a 2-period Cox-Ross-Rubinstein model consisting of a bank account B and a stock S. The risk-free interest rate for each time step is 2% and at each step the stock price either goes up by 10% or down by 10%. Assume S0 = 100 and correct all numbers up to two decimal places.
(a) Draw a tree showing all the trajectories of S and calculate the risk-neutral probability p★ (equivalent martingale measure).
[4 marks]
(b) Calculate the price of an European call option with strike price 95 at time t = 0.
Hint: The payoff for an European call option is given by
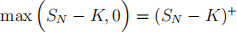
where K is the strike price.
[6 marks]
(c) Calculate the price of an Asian call option with strike price 97 at time t = 0. Hint: The payoff for an Asian call option is given by
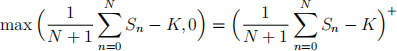
where K is the strike price.
[6 marks]
(d) Determine the perfect hedging strategy for the first period for the European call option with strike price 95.
[4 marks]
(2) Let Sn be the total assets of an insurance company at the end of year n. We suppose that Sn satisfies:
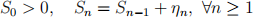
where the ηi are independent random variables, normally distributed with mean µ > 0 and variance σ 2 . We denote by B the event that the insurance company is bankrupt:
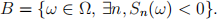
(a) Let M = (Mn )neN defined by
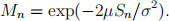
Show that M is a martingale with respect to the filtration generated by the ηi (扌n = σ(ηi , i = n)).
[6 marks]
(b) We define the stopping time τ = inf乒n : Sn < 0(. Justify that τ is a stopping
time and then show
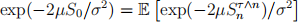
where Sτ An = (Sτ AnAk )keN .
[6 marks]
(c) Show that
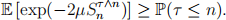
(Hint: Use the fact that Sτ An = Sτ < 0 when τ = n).
[4 marks]
(d) Prove the following bound for P(B):
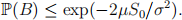
[4 marks]
(3) George and Hugo play a board game. The aim of each round is to capture opponent’s commander, which is a unique tile, hidden among many other tiles. For each round, Hugo wins with probability ![]() , otherwise George wins. The winner gets 50 points and the loser loses 50 points per round. A game is finished when one person wins two rounds in total. They sum up the points they gain or lose in each round and the final winner of the day is the player with more points.
, otherwise George wins. The winner gets 50 points and the loser loses 50 points per round. A game is finished when one person wins two rounds in total. They sum up the points they gain or lose in each round and the final winner of the day is the player with more points.
(a) Calculate the expected points (win/loss) for George in each game.
[8 marks]
(b) After losing 4 games consecutively and winning no game today, George
discovered a way to cheat by making a tiny mark on the edge of Hugo’s commander tile so that he can identify the tile at all time. Now they are going to play a final game for the day with 10 times the usual points. In this game, George cannot cheat in the first round as he can only mark the tile in the reshuffle phase after the first round. He can choose to mark the tile after first or second round and he will always cheat afterwards. If George cheated in the game, then he will win all the rounds afterwards. However, Hugo has a 40% chance to find out immediately after the game and in this case George loses the game in the worst possible case, i.e. a lose 1000 points to Hugo. George is not sure if he should take the risk, so he will make his decision by maximizing his expected points.
(i) Suppose George won 1 round and lost 1 round in this final game without cheating. By calculating the conditional expectations given he cheated or not in the third round, decide if he would cheat or not in the third round (i.e. mark the tile in between the second and third round) to maximize his expected points in the final game. [8 marks]
(ii) Suppose George won in the first round. Would he cheat in the second round
so that he can maximize his expected points in the final game? Calculate this maximum expected points. [6 marks] (iii) Determine the optimal strategy, i.e. the optimal time to start cheating (or not cheating at all) for George to maximize his expected points in the final game. Calculate the expected points for the final game using the strategy
you
found.
[8 marks]
(iv) What is the probability that George will be the winner of the day using the optimal strategy? Does this probability depend on the total points George lost in the first 4 games? [6 marks]
(4) James want to sell his house and would like to take the best offer in the market. Suppose there are N offers in the market. The offers only arrive sequentially, where he can examine each offer and then must decide whether to accept or reject it. Once rejected an offer cannot be reconsidered. For simplicity, assume the offers are independent and uniformly distributed on [500, 600]. Let X := 乒Xn (0SnSN by the sequence of offers.
(a) Write down the Snell envelope of X, denoted by Z := 乒Zn (0SnSN . [4 marks]
(b) (i) Compute E[ZN 21]. [4 marks]
(ii) Suppose Zn = max(Xn , an ) for some sequence 乒an (0SnSN. Using (b)(i) or
otherwise, prove that an satisfies the following recurrence relation:
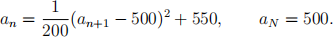
[6 marks] (c) Determine the stopping time τ at which James should accept an offer.
[4 marks]
(d) For each of the following list of offers, determine the offer accepted by James. Assume that there will be no more offers coming after the list ends in each situation. The lists are in chronological order.
(i) 540, 560, 580, 600;
(ii) 560, 550, 540, 530, 520;
(ii) 520, 580, 530, 570, 590, 560.
[6 marks]
2021-12-23