Coursework I-MTH203_AY2324
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Coursework I-MTH203_AY2324
Release Date: April 8 2024
Submission: 5:00pm April 15 2024
Instructions:
1. Sufficient details should be provided in your solutions to gain higher marks, round your answers to 3 decimal places if needed.
2. You are allowed to use online or computer tools if needed, but details (e.g., codes, snapshots) should be provided.
3. Sloppy submissions with unclear writing might cause mark reductions.
Question 1. [25 marks] XJTLU Library currently holds over 500,000 books, which are added to and updated throughout the year in response to requests from academic departments. Currently the library is planning a “buy-back” event to recycle used books from students, and it is believed that this would help reduce the cost on ordering brand new books from publishers. For the sake of simplicity, we categorize the daily business volume as “high” and “low” According to past experience, a day with high business volume is be followed by a day with high volume with probability 0.6; whereas a day with low volume will become high volume on the next day with probability 0.2. If the business volumes are high for consecutive 2 days, the library will need to spend $10,000 on new books, and $30,000 if the volumes are low for both days. If the business volume is changed from low to high, the library will spend $15,000 and $20,000 for “high-to-low” Besides the base case, the library would encourage students to participate the “buy-back” event by offering a lottery that awards 5 winners of the day. This will increase the probability of getting two consecutive high-volume days to 0.75 and there will be a 40% chance for a low volume day to change to a high-volume day. However, the cost will be increased by 20%.
(1) Write out the state space, the set of actions, the probability transition matrices and cost matrices. [8 marks]
(2) Write out a backward recursive formula to calculate fn (i), the optimal expected cost of stages n, n + 1, ⋯ , N, given state i at the beginning of stage n. [5 marks]
(3) Generate the optimal solution for XJTLU Library for a 3-day “buy-back” event, assuming the business volume of the day right before the event is low. Show your calculations and explain the optimal strategy. [12 marks]
Question 2. [25 marks] Use postgraduate application as the big background to design a multi-objective optimization problem and identify the Pareto-optimum. Make sure that your question contains 4 objectives and only finite number of feasible solutions.
Question 3. [25 marks] Below is the transition diagram for a queueing system.
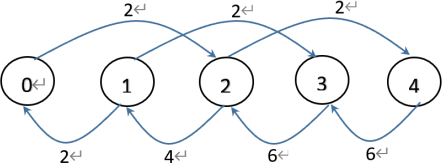
(1) Describe a queueing application that has the above diagram. Justify your choice with detailed explanations of the elements and parameters in the application. Your story should be written in a user-friendly way. [15 marks]
(2) List the balance equations for the system. [5 marks]
(3) What is the expected number of customers waiting to be served? [5 marks]
Question 4. [25 marks] A supermarket operates an online shop to deliver goods to customers who live close by. It is assumed that one customer will be served per delivery and the time needed to pick up and deliver goods for a customer follows an exponential distribution with a mean of 20 minutes, and customers arrive at a rate of 10 per hour, following a Poisson distribution. When all delivery personnel are occupied, newly arrived customers must wait. To win goodwill from the customers, the shop will pay s3 for every hour a customer waits for an available delivery person, The supermarket operates for 10 hours per day and pays each delivery person s50 per day.
(1) Based on the provided information, identify the cost function and determine the number of delivery person the shop should hire. [10 marks]
(2) Suppose that the manager has newly decided to only accept a maximum of customers at a time, including those currently being serviced.
(a) How would it affect the customer waiting time, delivery person’sutilization, and the business in general?
(b) Again determine the number of delivery person the shop should hire but
consider conditions different from those in (1). For example, different type of costs or target service levels. Introduce additional parameters and assumptions if you need. Avoid trivial settings. [15 marks]
2024-04-12