STAT 244 Midterm
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
STAT 244 Midterm
1. [6 points] Suppose we draw two cards without replacement from a standard deck (52 cards, 26 red and 26 black). Let X = 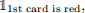 i.e., the indicator variable for the event that the first card is red, and similarly let Y =
i.e., the indicator variable for the event that the first card is red, and similarly let Y =  Then Corr(X, Y ) is:
Then Corr(X, Y ) is:
(a) Zero, and X and Y are independent
(b) Zero, but X and Y are not independent
(c) Positive
(d) Negative
Choose your answer, and explain briefly. (Note—you do not need to numerically calculate the corre-lation/covariance to answer this question.)
2. [6 points] Let A and B be two events. Is the following statement correct:
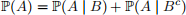
(a) Yes, this statement is always true, for any events A and B.
(b) No, in general this statement is not true.
Choose your answer, and explain in your own words why it is correct or not correct.
3. [6 points] Suppose X is drawn from a distribution with the following density:
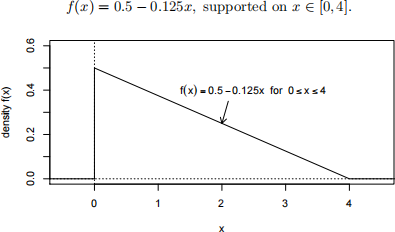
Let I be the integer part of X, and let D be the decimal part of X, so that X = I + D. For example if we draw X = 2.3456, then I = 2 and D = 0.3456.
Which statement is true about E(D), the expected value of D?
(a) E(D) < 0.5
(b) E(D) = 0.5
(c) E(D) > 0.5
Choose your answer, and explain briefly. (Note—you do not need to numerically calculate the expected value to answer this question.)
4. [6 points] Let X, I, and D be defined as in the previous problem. Which statement is correct?
(a) I and D are independent.
(b) I and D are not independent.
Choose your answer, and explain briefly.
5. [8 points] Patients showing symptoms of a disease are given a blood test which can give two results, positive or negative. Suppose that the test has the following accuracy levels:
● For a healthy patient, the test has a 2% chance of a positive result.
● For a diseased patient, the test has a 90% chance of a positive result.
Suppose that 4% of the population being tested, actually has the disease.
If a patient receives a positive result on the test, what is the probability that this patient has the disease?
6. [16 points total] Suppose you have 26 cards labeled with the letters A through Z, shuffled at random. You draw cards one at a time without replacement.
(a) [8 points] For any integer k between 1 and 26, let Ak be the event that the first k letters are in alphabetical order. For example, if k = 3 and your first three draws are B, then D, then Z, then the event has occurred, while if your first three draws are B, then Z, then D, then the event has not occurred.
Calculate P(Ak).
(b) [8 points] Let T be the length of time for which alphabetical order was maintained. For example, if your draws are B, D, Z, M, A, ... then T = 3 because the 4th draw (the letter M) was the first one that violated alphabetical order. What is the distribution of T?
7. [20 points total] Let X and Z be independent draws from a Exponential(1) distribution. This distribution has density e−x on x ∈ (0, ∞), CDF 1 − e−x, mean 1, and variance 1.
(a) [6 points] Let A = (X − Z)2 and calculate E(A).
(b) [8 points] Let
Find either the CDF of Y , FY(y), or the density of Y , fY(y), and also state the support of Y, i.e. the range of possible values. You do not need to compute both the CDF and the density.
(c) [6 points] Multiple choice—what is the correlation, Corr(X, Y)? Circle one:
i. Equal to −1.
ii. Negative, but not −1.
iii. Equal to 0.
iv. Positive, but not 1.
v. Equal to 1.
Briefly explain your answer. It is not required to explicitly calculate the correlation.
8. [11 points total] Let X be drawn from the Uniform[0, 1] distribution, and then conditional on X, let Y be drawn from the Uniform[0, X] distribution.
(a) [4 points] What is the support of the pair of random variables (X, Y)? To answer this question, you can either express your answer mathematically (using equations/inequalities/intervals/etc), or you can sketch the region on a graph.
(b) [7 points] What is the joint density of (X, Y)?
9. [21 points total] You call a dentist to make an appointment. When you call, you are randomly assigned either to phone line #1 or phone line #2 (50% chance for each). The amount of time (in minutes) that it takes for someone to pick up the phone is distributed as Exponential(0.1) for phone line #1, or as Exponential(0.2) for phone line #2. (Recall the density of the Exponential(λ) distribution is λe−λt on t ∈ (0, ∞), its CDF is 1 − e−λt, its mean is 1/λ, and its variance is 1/λ2 .)
(a) [8 points] What’s the expected value and the variance of T, the length of time you have to wait for someone to pick up the phone?
(b) [5 points] What’s the probability that, after 10 minutes, you’re still waiting?
(c) [8 points] If after t minutes (for some positive constant t), you’re still waiting, what’s the prob-ability that your call was assigned to phone line #1? Describe how this probability changes, as t goes from zero to infinity (i.e., as you wait longer and longer).
2021-10-31