EECS 334 – W24 Principles of Optics Homework 1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
EECS 334 – W24
Principles of Optics
Homework 1
Set: 01/18/24
Due date: 01/25/23 at 5pm ET
General advice regarding homework: No credit will be given for a correct answer that does not clearly show your work. Write down every step of your thought process. Diagrams/figures encouraged (sometimes required). Remember units.
Total = 39 points
1. [4 points]
To determine the refractive indexof a transparent plate of glass, a microscope is first focused on a tiny scratch in the upper surface, and the barrel position is recorded. Upon further lowering the microscope barrel by 1.29 mm,a focused image of the scratch is seen again. (Note the microscope “barrel” moving up or down changes the imaging plane it observes.) The plate thickness is 1.0 mm and the plate of glass and microscope setup is in air.
What is the reason for the second image?
What is the refractive indexof the glass?
2. [4 points]
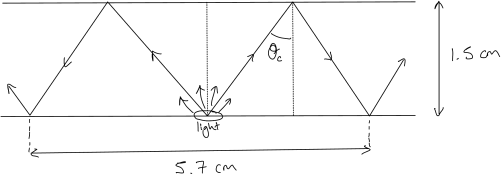
A small source of light at the bottom face of a rectangular glass slab 1.5cm thick is viewed from above. Rays of light totally internally reflected at the top surface outline a circle of 5.70 cm in diameter on the bottom surface. The critical angle is labeled ![]() ‘ in the sketch. Determine the refractive indexof the glass.
‘ in the sketch. Determine the refractive indexof the glass.
3. [6 points]
Show that the lateral displacement d of a ray of light penetrating a rectangular plate of thickness tin air is given by
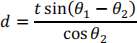
Where θ1 and θ2 are the angles of incidence and refraction, respectively. Find the displacement when t = 4 cm, n = 1.50, and θ1 = 50° . (Lateral displacement is the perpendicular distance between the incident ray and the emergent
ray.)
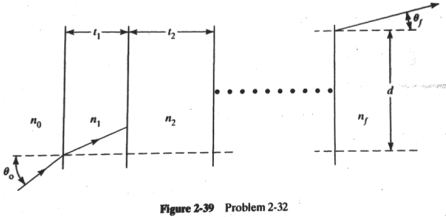
4. [3 points]
A ray of light traverses successively a series of plane interfaces, all parallel to one another and separating regions of differing thickness and refractive index.
a. Show that Snell’s law holds between the first and last regions, as if the intervening regions did not exist.
b. Calculate the net lateral displacement (d) of the ray from point of incidence to point of emergence. (Here, the lateral displacement is with respect to the incoming and exit positions on the surfaces.
Indicated on figure as d.)
5. [7 points]
A meter stick (i.e. a stick that is 100 cm long) lies along the optical axis of a convex mirror of with a radius of curvature of 60 cm, with its nearer end 45 cm from the mirror surface. How long is the image of the meter stick?
(Include a sketch, with labels, to setup the problem.)
6. [6 points]
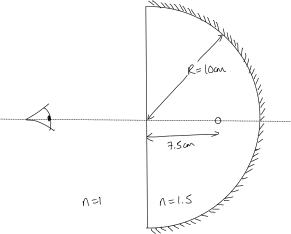
A glass hemisphere is silvered over its curved surface. A small air bubble in the glass is located on the central axis through the hemisphere 7.5 cm from the plane surface. The radius of curvature of the spherical surface is 10 cm, and the glass has an indexof 1.50. Looking along the axis into the plane surface, one sees two images of the bubble. How do they arise and where do they appear? (Consider each interface as the rays see them for the calculations.)
7. [9 points]
A concave mirror forms animage on a screen twice as large as the object.
Both object and screen are then moved to produce animage on the screen that is three times the size of the object. If the screen is moved 60 cm in the process, how far is the object moved? What is the focal length of the mirror?
2024-01-27