EEEM062: Applied Mathematics for Communication Systems Semester 1 2021/2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Faculty of Engineering & Physical Sciences
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Undergraduate Programmes in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
EEEM062: Applied Mathematics for Communication Systems
FHEQ Level 7 Examination
Semester 1 2021/2
Q1.
(a) In probability and statistics, explain what the cumulative density function (cdf) is and how it can be used to calculate the probability of a random variable to get values in a specific range. [15%]
(b) Give an example of calculating the mean value of a random variable of your choice and explain in your own words what the meaning of this mean value is. [15%]
(c) Explain if Figure 1 below shows the graph of a probability density function (pdf) or of a cumulative distribution function (cdf).
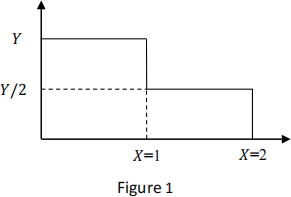
[10%]
(d) For the pdf or cdf of Figure 1, find the probability that the random variable x takes values larger than 1.5. Justify your answer. [20%]
(e) Assume a wireless communication system where the symbols -1 and 1 are transmitted independently and with equal probability. In addition, assume that during their transmission, the symbols are affected by independently distributed additive noise with its pdf given in Figure 2.
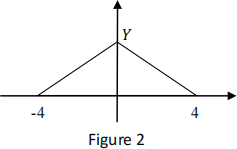
Calculate the mean the and variance of the additive noise of Figure 2. [20%]
(f) Explain how you would perform detection of the transmitted symbols and calculate the corresponding probability of error. [20%]
Q2
(a) In estimation theory,
(i) give two characteristics a good estimator should have and explain in your own words why these characteristics are required. [15%]
(ii) Explain in your own words what the Cramer Rao Bound is and how it can be used to judge how good an estimator is. [15%]
(iii) Assume that you want to estimate an unknown parameter by using a noisy
received signal for which you know the mean value and the covariance matrix of the noise but not its probability density function (pdf). You also know that the relationship between the unknown parameter and the received signal is linear. Would you use the BLUE estimation method, or the Maximum Likelihood estimation method? Justify your answer. [10%]
(b) The signals {x [0], … , x [N − 1]} are observed, that are independent and normally
distributed with a zero mean and a variance of σ2 . To estimate the variance, we use the following estimator:
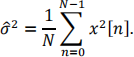
Explain if this is an unbiased estimator. [15%]
(c) Consider the observations x[n] = ATn + w [n] with n = 0, … , N − 1, where A is a
parameter to be estimated, w [n] is additive white Gaussian noise of variance σ2 and T is a known parameter taking values larger than one (T > 1).
(i) Write the joint probability density function for the whole set of observations and a given value of the unknown parameter A. [15%]
(ii) Calculate the Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) for A, when N = 4, T = 2 and σ 2 = 1. [20%]
(iii) Find an estimator that meets the CRLB. [10%]
Q3.
(a) Explain which concept of linear algebra is very useful for understanding multiple antenna communication (in a maximum of 100 words). [10%]
(b) Explain which concept of linear algebra can be used to implement beamforming in multiple antenna communication (in a maximum of 100 words). [10%]
(c) Let 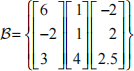 be a set of vectors. Can this set of vectors be a basis of R3 ?
be a set of vectors. Can this set of vectors be a basis of R3 ?
Justify your answers by providing all the details of your calculations. [20%]
(d) A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system use the Eigen decomposition
process to parallelise the MIMO channel 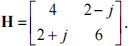 The Eigen decomposition process is performed at the receiver, where one part of the decomposition is feedback at the transmitter to precode the transmit signal s = [ − 1 + j 1 + j ]T and another part is used at the receiver to equalise the received signal. Assuming that the noise is such that n = [ − 1.2 + 0.5j 0.1 − 2.5j]T , calculate the value of the received signal after the equalisation process. Justify your answers by providing all the details of your calculations. [30%]
The Eigen decomposition process is performed at the receiver, where one part of the decomposition is feedback at the transmitter to precode the transmit signal s = [ − 1 + j 1 + j ]T and another part is used at the receiver to equalise the received signal. Assuming that the noise is such that n = [ − 1.2 + 0.5j 0.1 − 2.5j]T , calculate the value of the received signal after the equalisation process. Justify your answers by providing all the details of your calculations. [30%]
(e) Let A and B be two invertible square matrices. Determine through derivation if the equality A(A +B)− 1 B = B (A +B)− 1 A is correct. Justify your answer by providing all the details of your derivation. [15%]
(f) Let 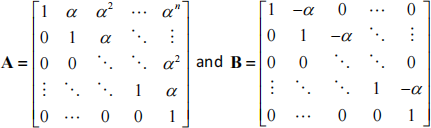 be two nxn matrices.
be two nxn matrices.
Determine through derivation if the equality A −2AT = A − 1BAT is correct. Justify your answer by providing all the details of your derivation. [15%]
2024-01-19