EEEM062: Applied Mathematics for Communication Systems Semester 1 2019/20
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Faculty of Engineering & Physical Sciences
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Postgraduate Programmes in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
EEEM062: Applied Mathematics for Communication Systems
FHEQ Level 7 examination
Semester 1 2019/20
Q1.
(a) In probability theory and statistics,
(i) explain what the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of a real-valued random variable describes. [10 %]
(ii) Give the equation relating the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of a real-valued random variable to its probability density function (pdf). [10 %]
(iii) Show how the expected value and the variance of a real-valued continuous random variable can be computed as a function of the probability density function. [10 %]
(iv) Assume the following function
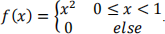
Can f(x) be a cumulative distribution function? Explain why. [15 %]
(b) In Matlab we use the function “rand” to produce samples of a uniformly distributed random variable X in the interval (0,1).
(i) Write a Matlab script that uses the function “rand” to produce a sequence of randomly generated - 1 or 1 symbols, that are statistically independent and their probability of appearance of - 1 is P(- 1)=0.25. Explain your solution. [15 %]
(ii) Calculate the mean theoretical value of the random variable Y=3X. [10 %]
(iii) If we produce random samples by using theMatlab function 4*rand- 1, calculate the pdf of these random samples and calculate the probability of producing a sample with a value smaller than 0. [30 %]
Q2.
(a) In estimation theory,
(i) explain if there is any minimum in the variance of unbiased estimators. [10 %]
(ii) Explain what a Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator (MVUB) is and explain if a MVUB always meets the Cramer-Rao Lower Bound. [15 %]
(iii) Explain what the Best Linear Unbiased Estimator (BLUE) is and what prior knowledge is needed in advance to determine it. [15 %]
(iv) Assume that you want to estimate an unknown parameter by using a noisy received signal for which you know the mean value and the covariance matrix of the noise but not its probability density function (pdf). You also know that the relationship between the unknown parameter and the received signal is linear. Would you use the BLUE estimation method, or the Maximum Likelihood estimation method? Justify your answer. [15 %]
(v) For the estimation problem of part (iv) explain if your estimator reaches the Cramer- Rao Lower Bound. [10 %]
(b) Consider the observations x[n] = A + w [n] with n = 0, … , N − 1, where A is a parameter to be estimated and w[n] is an additive white Gaussian noise of variance σ2 .
(i) Write the probability density function of the vector x = [x0 … xN − 1]T for a given value of A. [15 %]
(ii) Calculate the Cramer-Rao Lower Bound for this estimation problem of finding A from x [n]. [20 %]
Q3.
(a) Explain (in 2 or 3 sentences) the difference between a deterministic and a random signal. [10 %]
(b) Let s (t ) be a time domain signal and α be a parameter, such that α >1 . Match each of the following modified mathematical definition of s(t) (1st column of Table Q3.b) with their correct corresponding effect on s(t ) (2nd column of Table Q3.b).
Table Q3.b
|
|
Effects |
|
a) αs (t ) |
1) Compression |
|
b) s (t ) |
2) Amplification |
|
c) s (αt) |
3) Reflection |
|
d) s (t |
4) Expansion |
|
e) s ( − t ) |
5) Attenuation |
[15 %]
(c) Explain (in 1 or 2 sentences) what filtering is, in signal processing. [10 %]
(d) 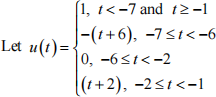 be a time domain signal.
be a time domain signal.
(i) Draw the signal u (t ) . [10 %]
(ii) Draw the signal u (t − 4) and determine if it is an even signal. Justify your answer. [10 %]
(e) Let 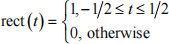 be a time domain signal. Derive its auto-correlation function. [20 %]
be a time domain signal. Derive its auto-correlation function. [20 %]
(f) Does shifting a signal in the time domain modifies the content of its frequency information. Justify your answer. [10 %]
(g) Determine the type of signal that will result from the convolution of a sinus cardinal waveform with a direct current (dc) signal. Justify your answer. [15 %]
2024-01-15