Midterm
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Instructions
• Do not work with one another or consult any materials during the test
• All of the numbers on this test are generated algorithmically
• The use of x1, x2, . . . throughout this document are as placeholders
– e.g., a problem may state that “the price of A in Domestic is x3”
• The actual values for x1, x2, . . . are on your individualized test in Tests & Quizzes
– e.g., your test will tell you that x3 = 5
• When rounding numeric answers, more decimal places is better. Three is good
– Answers within ±0.1 of the correct answer will be considered correct
• For multiple choice problems, report numbers instead of letters (e.g., “1” instead of “A”)
• This midterm consists of 15 equally-weighted sub-parts
• Upload pictures of your work to Assignments → Midterm Rough Work
Problem 1
Consider two countries, Limgrave and Caelid, in a Ricardian setting. Suppose Limgrave has x1 workers and Caelid has x2 workers. The output that one worker can produce in each country in terms of each good is given in the following table:
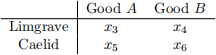
1.1 Which of the following statements is true?
1. Limgrave has a comparative advantage in A.
2. Foreign has a comparative advantage in A.
3. Limgrave has a comparative advantage in A and B.
4. Neither country has a comparative advantage in A.
1.2 What is the total number of A that will be produced in the free-trade equilibrium?
1.3 What is the Limgrave’s real wage in terms of their imports in free-trade with PA W /PB W = x7?
1.4 Which of the following statements is true?
1. Immigration causes real wages to unambiguously rise.
2. Immigration causes real wages to unambiguously fall.
3. Immigration causes no change in real wages.
4. The effect of immigration on real wages is ambiguous.
Problem 2
Consider a Specific-Factors framework where Limgrave produces two goods, A and B, using high-skilled labor, L, and low-skilled labor, L. Suppose that, in autarky, the following is true:
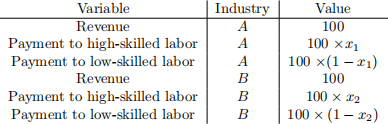
Suppose that Limgrave decides to open to trade with Caelid. Doing so causes the price of B to remain unchanged, but the price of A falls by x3% and the nominal wage rate falls by x4% (be careful with the negatives here!) In the short-run, high-skilled labor cannot move across industries.
2.1 By what percent does the wage rate of high-skilled labor change in the A industry?
2.2 By what percent does the wage rate of low-skilled labor change in the B industry?
2.3 If Limgrave engages in free trade:
1. Low-skilled workers will unambiguously be made better off.
2. Low-skilled workers will unambiguously be made worse off.
3. The effect on low-skilled workers will be indeterminate.
4. Low-skilled workers will be no better or worse off.
Problem 3
Consider a Heckscher-Ohlin framework. Limgrave produces two goods, A and B, using labor, L, and capital, K. Limgrave has x1 workers and x2 machines. For convenience, suppose that the wage rate and rental rate of capital are both equal to 1 in equilibrium, w = r = 1. Production of each good takes the following form:
A = x3LA + x4KA (1)
B = x5LB + x6KB (2)
3.1 Which industry in labor-intensive?
1. A.
2. B.
3. Both.
4. Neither.
3.2 How many workers will be employed in the A industry in equilibrium?
3.3 What will the price of B be in the no-trade equilibrium?
3.4 Immigration of workers into Limgrave will result in:
1. an increase in production of A, and a decrease in production of B.
2. a decrease in production of A, and an increase in production of B.
3. an increase in production of A, and an increase in production of B.
4. a decrease in production of A, and a decrease in production of B.
5. an increase in production of A, and no change in the production of B.
6. a decrease in production of A, and no change in the production of B.
7. an increase in production of A, and no change in the production of B.
8. a decrease in production of A, and no change in the production of B.
Problem 4
The following are a set of multiple choice questions based on new trade theory.
4.1 Suppose a firm faces a demand curve P = 100 − x1 × Q. The slope of the firm’s marginal revenue curve, provided P > 0 and Q > 0, will be:
1. Greater than or equal to −x1
2. Smaller than −x1
4.2 From the table below, which industry is harder to rationalize with old trade theory models?
1. Agriculture
2. Manufacturing
3. Raw materials

4.3 New trade theory argues that differences across countries is one of the main reasons why they trade.
1. True
2. False
4.4 New trade theory argues that minimizing differences across countries will maximize the gains from trade.
1. True
2. False
2023-12-25