MAT3010 Assignment 3 NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING 2
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
MAT3010 (HUI Shen): Assignment 3
Due: 2023/11/27
STATIC OPTIMIZATION: NONLINEAR PROGRAMMING 2
Question 1
(12 points) Solve the following consumer demand problem where, in addition to the budget con-straint, there is an upper limit 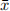 which rations how much of the first good can be bought:
which rations how much of the first good can be bought:
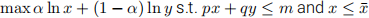
Show that the candidate you find is indeed the solution of the problem.
Question 2
(10 points) Consider the problem max 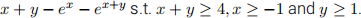
(a) (3 points) Sketch the admissible set S.
(b) (4 points) Find all pairs (x, y) that satisfy all the necessary conditions.
(c) (3 points) Find the solution to the problem.
Question 3
(12 points)
(a) (4 points) Consider the nonlinear programming problem (where c is a positive constant)
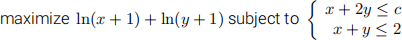
Write down the necessary Kuhn-Tucker conditions for a point (x, y) to be a solution of the problem.
(b) (4 points) Solve the problem for c = 5/2.
(c) (4 points) Let V (c) denote the value function. Find the value of V' (5/2).
Question 4
(10 points) Solve the following problem (assuming it has a solution)
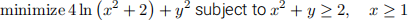
Question 5
(14 points)
(a) (9 points) Solve the following problem for all values of the constant c :
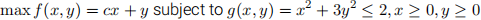
(b) (5 points) Let f*(c) denote the value function. Verify that it is continuous. Check if (6.10) holds.
Question 6
(16 points) Consider the following optimization problem.
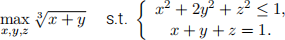
Call it Problem 1.
(a) (3 points) Show that the above problem has the same solution(s) as the following one:
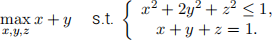
(b) (5 points) Show that the optimization problem in (a) has the same solution(s) as the follow-ing one:
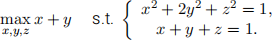
Call it Problem 2.
(c) (8 points) Now that we have shown that Problem One and Problem Two are equivalent. Solve Problem One by studying Problem Two. In particular, does the CQ condition give additional solution candidates?
Question 7
(10 points) Consider the problem 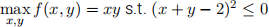
Explain why the solution is (x, y) = (1, 1). Verify that the Kuhn-Tucker conditions are not satisfied for any λ, and that the CQ fails at (1,1). (Hence the K-T method doesn’t work.)
Question 8
(16 points) Consider the Problem 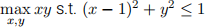
(a) (8 points) Solve the problem using the Kuhn-Tucker method.
(b) (8 points) The Kuhn-Tucker conditions give you two solution candidates. The one with the largest function value is the solution. Is the other, i.e., the one that gives the lowest function value the solution to the following minimization problem?
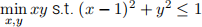
If not, what’s the correct answer?
2023-11-29