MATH1021: Calculus of one variable Assignment 2 Semester 2, 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Assignment 2
MATH1021: Calculus of one variable
Semester 2, 2023
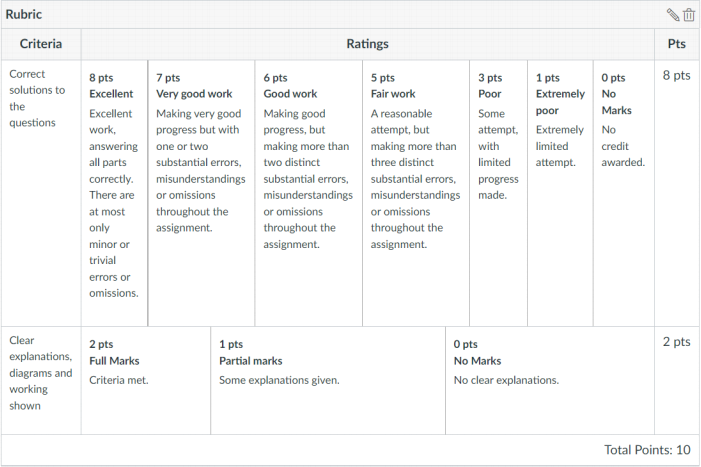
This assignment is worth 10% of your final assessment for this course. Your answers should be well written, neat, thoughtful, mathematically concise, and a pleasure to read. Please cite any resources used and show all working. Present your arguments clearly using words of explanation and diagrams where relevant. After all, mathematics is about communicating your ideas. This is a worthwhile skill which takes time and effort to master. The marker will give you feedback and allocate an overall mark to your assignment using the following criteria:
![]() 1. We define a function f : [−1, 1] → R by
1. We define a function f : [−1, 1] → R by
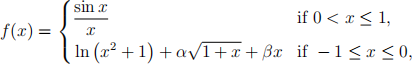
where α,β ∈ R are constants such that f is continuous and also differentiable at x = 0.
(a) tha(Det)t(e)![]() x
x![]() iven prop(for every)ert(x)ie(∈)s.(
iven prop(for every)ert(x)ie(∈)s.( ![]()
![]()
![]() e1
e1![]() alue of(Find) f′(th)
alue of(Find) f′(th)![]()
![]() ?(o)nstants α and β such
?(o)nstants α and β such
(b) f(L)![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 0(fo(−)r(1) ,al(0)
0(fo(−)r(1) ,al(0)![]() x(b)
x(b)![]()
![]()
![]() 1(i)
1(i)![]()
![]() ryD(.)etermine l(Compute)imx(f′′)
ryD(.)etermine l(Compute)imx(f′′)![]()
![]() 1
1![]() f(d)′′
f(d)′′ ![]()
![]() (
(![]()
![]() im(He)
im(He)![]()
![]() f(s)
f(s)![]()
![]()
![]() .that
.that
(c) Using part (b) and the Intermediate Value Theorem, conclude that on the interval (−1, 0), the function f has a unique inflection point, say x0 .
(d) Find limx→ (− 1)+ f′ (x) and using parts (a) and (c), deduce that on the interval − 1 < x < 0, the function f has a unique critical point x1 with x1 < x0 .
(e) ![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
concavity and points of inflection, if any).
2. Define the function g : [0, 1] → R by
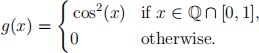
(a) For any positive integer N ≥ 1, find the lower Riemann sum LN and upper Rie- mann sum UN for the function g on [0, 1]. [Use without proof that between any two real numbers a and b with a < b, there is an irrational number.]
(b) Determine limN→∞ LN and limN→∞ UN . Then, conclude whether g is Riemann integrable over [0, 1] or not.
3. (a) Find the second-order Taylor polynomial P2 (x) for the function ![]() about x = 0. [Hint: Use the whole Taylor series of sin x.]
about x = 0. [Hint: Use the whole Taylor series of sin x.]
(b) If R2 (x) = ![]() − P2 (x) is the remainder of the second-order Taylor polynomial
− P2 (x) is the remainder of the second-order Taylor polynomial
P2 (x) of ![]() , show that 0 < R2 (x) <
, show that 0 < R2 (x) < ![]() for all x ∈ (0, 0.5]. Then, conclude that
for all x ∈ (0, 0.5]. Then, conclude that
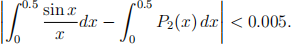
(c) Hence, find l00.5 ![]() dx with an error less than 0.005. Write your answer to three decimal digits (rounding to the nearest thousandth).
dx with an error less than 0.005. Write your answer to three decimal digits (rounding to the nearest thousandth).
2023-10-17