ECON30019 Assignment 1 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON30019 Assignment 1
Due at 11:59 pm on Aug 17, 2023
Question 1. (36 points)
Below are the choices made by Albert, Brittney, and Calvin when choosing from different sets of fruits.

1. (6 points) Can Albert’s choices be represented by any utility function? If so, find a utility function that represents his choices. If not, explain why by finding contradictions in the implications of his choices.
2. (6 points) Do Albert’s choices violate Axiom α or β?
3. (6 points) Can Brittney’s choices be represented by any utility function? If so, find a utility function that represents her choices. If not, explain why by finding contradictions in the implications of her choices.
4. (6 points) Do Brittney’s choices violate Axiom α or β?
5. (6 points) Can Calvin’s choices be represented by any utility function? If so, find a utility function that represents his choices. If not, explain why by finding contradictions in the implications of his choices.
6. (6 points) Do Calvin’s choices violate Axiom α or β?
Question 2. (31 points)
Suppose in an experiment, you randomly hand out a chocolate to half of the subjects in a large group. You then allow the subjects to trade the chocolate. That is, the ones who own the chocolate can sell theirs, and the ones who do not own the chocolate can buy from the others. The chocolates can be sold at any price the buyer and the seller agree upon, irrespective of the price in the shop.
1. (9 points) Explain why, in the absence of transaction costs, we would expect about half of the chocolates to change hands according to the standard theory.
2. (8 points) Suppose that a subject, who received a chocolate in the exper-iment, has the following value function for chocolate and for money:
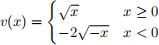
What is the minimum price she is willing to accept to sell her chocolate?
3. (8 points) Suppose that a subject, who did not receive a chocolate in the experiment, has the same value function for chocolate and for money:
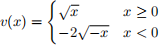
What is the maximum price she is willing to pay to buy a chocolate?
4. (6 points) When the experiment is conducted in the lab, you observed that less than half of the chocolates changed hands. Use your answers to Questions (2.2) and (2.3) to explain this observation.
Question 3. (33 points)
A Capuchin monkey’s preference over cF units of fruit discs and cC units of cereal chunks can be represented by the utility function
u (cF , cC ) = cF + cC + µ (cF − rF ) + µ (cC − rC )
where rF is his reference point for fruit discs, and rC is his reference point for cereal chunks. The function µ (·) is defined as
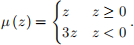
The reference point is the status quo (that is, the monkey’s initial endowment).
1. (10 points) Suppose that the monkey has one fruit disc and no cereal chunks. What is the minimum number of cereal chunks the monkey would require in order to trade away his fruit disc?
2. (10 points) Suppose that the monkey has cF fruit discs and cC cereal chunks. What is the minimum number of fruit discs the monkey would require in order to trade away one of his cereal chunks?
3. (10 points) Suppose that the monkey has nothing and is asked to choose between receiving fruit discs or receiving cereal chunks. What is the min-imum number of cereal chunks the monkey would be willing to accept instead of receiving one fruit disc?
4. (3 points) Use the concepts we discussed in class to explain your answers to Questions (3.1), (3.2), and (3.3).
2023-08-15