ECO00056M Fixed Income Securities MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECO00056M
MSc Degree Examinations 2018-9
Economics
Fixed Income securities
Answer any THREE questions
1.
(a) [5O marks] Assume that today is 15 May 2OOO. You observe the following bond prices:
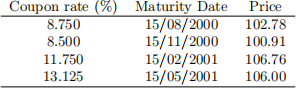
Assume that the quoted prices are ‘dirty,, i.e. they already include the accrued
interest. All bonds pay coupons semi-annually. using the bootstrap procedure, for the maturities spanning 1 year (i.e. for Ti = O.25)O.5O)O.75)1), calculate:
. Discount factors, Z(O)Ti ),
. Semi-annually compounded rates, T2 (O)Ti ),
. continuously compounded rate, T (O)Ti ).
(b) [3O marks] consider two STRIPS: one has 3-years to maturity and yields a
continuously compounded rate T (O)3) = 1O%, while the second has 5 years to maturity and yields a continuously compounded rate T (O)5) = 5%. Discuss whether this scenario is consistent with the no-arbitrage principle and, if not, what arbitrage strategy could be set up to gain from the mispricing.
(c) [2O marks] A client is reviewing a year-end portfolio report. Since the beginning of the year, market yields have increased slightly. In comparing the beginning-of-the-year
price for the bonds selling at a discount from par value to the end-of-year prices, the client observes that all the prices are higher. The client is perplexed since he expected that the price of all bonds should be lower since interest rates increased. How can you explain to the client, why the prices of the bonds in the portfolio selling at discount
have increase in value?
2.
(a) [5O marks] The current, continuously annually compounded yield curve is as in the following table:
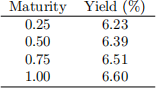
calculate the duration and convexity for the following securities:
. O.5-year zero coupon bond
. 1-year loating rate bond with 2O basis point spread, paid semi-annually
. O.75-year coupon bond paying 3% quarterly
(b) [3O marks] Explain why you agree or disagree with the following statement:”If the
term structure of interest rates is lat and two bonds have the same duration, then the percentage change in price of the two bonds will be the same for a given (parallel)
change in interest rates”.
(c) [2O marks] you observe the following term structure of interest rates:
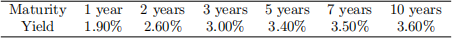
compute the level factor, the slope and the butterly spread. [Note: for the butterly spread use the 5-year yield.]
3. on 3O June 2O18 you observe the continuously compounded yield curve as in the following table:
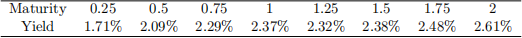
on this date a inancial institution purchases $1OO million worth of a 2-year Treasury note paying a 2.88% coupon semi-annually priced at $1OO.5O. At the same time the inancial
institution enters into a forward contract with the seller of the Treasury note in which it will sell the same T-note three months later (no accrued interest payments will be made).
(a) [2O marks] How many bonds does the inancial institution purchase?
(b) [5O marks] what is the quoted forward price for the Treasuries in three months,
Pc(f wd)(O)O.25)2)?
(c) [3O marks] Recall that the outright purchase of a Treasury note plus the forward
contract is similar to a repo agreement. calculate the implied repo rate for this 2 -year Treasury note?
4. you observe the continuously compounded Teal yield curve as in the following table:
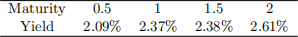
(a) [5O marks] compute the price of a TIPS security with 2 years to maturity, a 2% coupon rate paid semi-annually and index ratio 1.O725.
(b) [3O marks] If the TIPS security considered in (a) was issued two years ago, what has been the continuously compounded inlation rate over this period? [Note: ignore the inlation measurement lag.]
(c) [2O marks] Assume that the annual inlation rate has a normal distribution
![]()
![]() π … N (π , σπ(2)), where π = O.O3 and σπ(2) = O.OOO4. If the 1-year real rate is O.O2O9, the
π … N (π , σπ(2)), where π = O.O3 and σπ(2) = O.OOO4. If the 1-year real rate is O.O2O9, the
1-year nominal rate is O.O557 (both continuously compounded), what is the implied inlation risk premium K?
5. consider the interest rate tree as in the following table:
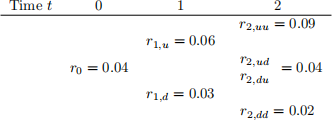
All entries are continuously compounded interest rates. The risk-neutral probability of moving up the tree is constant and equal to O.7.
(a) [5O marks] An investor buys the 3-year zero coupon bond at time t = O. what is her 1-year e从pected return on the investment, as of t = O, if the natural probability of
moving up the tree is O.3?
(b) [5O marks] consider a 3-year range bond, with a coupon equal to $1O per year. The range bond pays the coupon at time t if the continuously compounded rate at time
t - 1 is within the interval [T , T] = [O.O25, O.O5] and zero otherwise. compute the value of the range bond at time t = O.
2023-07-31