ECO00056M Fixed Income Securities MSc Degree Examinations 2020–21
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECO00056M
MSc Degree Examinations 2020–21
Economics
Fixed Income Securities
Answer any THREE questions
1.
(a) [25 marks] From the following data obtain the discount curve:
• A zero coupon bond paying Pz (0, 0.5) = 99.20.
• A coupon bond paying 3% quarterly P(0, 0.25) = 100.5485.
• A coupon bond paying 6% quarterly P(0, 0.75) = 103.1655.
• A coupon bond paying 5% semiannually P(0, 1) = 103.0325.
(b) [25 marks] Calculate the yield to maturity on the 1 −year bond from (a).
(c) [25 marks] In addition to bonds in (a) you also find the following 1.5 −year that pays coupons seminannually:
• A coupon bond paying 3% semiannually P(0, 1.5) = 103.0325.
Is the price of this bond consistent with the no-arbitrage principle? Explain and give an example of an arbitrage strategy if the arbitrage opportunity exists. Assume that all zero-coupon bonds with all maturities can by sythesized.
(d) [25 marks] What is the advantage of a factor model?
2. Use the following continuously compounded yields when needed:
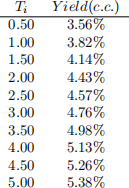
(a) [40 marks] You hold the following portfolio:
• Long $30 million of a 4 −year floating rate bond with a 45 basis point spread paid semiannually;
• Short $30 million of a 3 −year fixed coupon bond paying 4% semiannually.
Compute the dollar duration of the portfolio.
(b) [60 marks] You are worried about interest rate volatility. You decided to hedge your portfolio taking into account duration and convexity with the following bonds:
• A 6 − month zero coupon bond
• A 5 −year zero coupon bond
How much should you go short/long on these bonds in order to make the portfolio immune to interest rate changes? What is the value of the hedged portfolio?
3. Suppose that on the 15th March 2021 you want to enter into a forward contract to purchase 3 −year Treasury bond with coupon rate 3% in four years. Use the yields data in the following table.
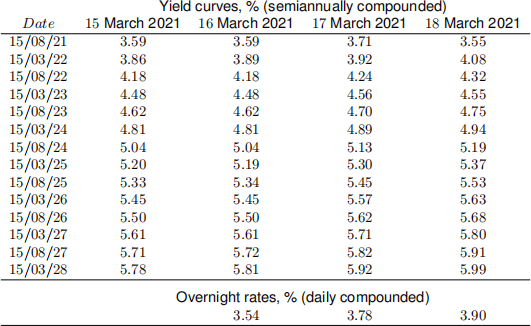
(a) [25 marks] Compute the forward price of the contract as of 15th March 2021.
(b) [25 marks] Compute the value of the forward contract that you entered on 15th March on each of the next three days.
(c) [25 marks] Assume the firm and the counterparty mark to market the forward contract. Calculate the cash flows (i.e. daily profit or loss) between the counterparties over time.
(d) [25 marks] The bottom panel of the data table contains overnight rates. Compute the total
profit/loss on the contract at the end of each day. [Note: the daily overnight rate is quoted using 360 days in a year convention.]
4. Suppose today you observe the following continuously compounded forward rates:
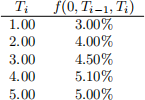
(a) [25 marks] Find spot yields r(0, Ti ).
(b) [50 marks] Assume that the market expects that the short 1 −year rate in 1 year will increase to 3.5%. Assuming that the distribution of r(1, 2) conditional on today’s information is normal with variance 1%, that is
r(1, 2) ∼ N(0.035, 0.01),
calculate the expected yield, convexity and risk premium implied by the currently observed market 2 −year yield. Does the Expectation Hypothesis hold? What is the log risk premium? [Hint: Given x ∼ N(µ,σ2 ), and a constant A, we have E[eAx] = e![]()
(c) [25 marks] Now assume that the Expectations Hypothesis holds but we do not know the market expectation of the future 1 −year rate. If we still observe the spot curve r(0, 1) = 3% and the
variance of the 1 −year rate 0.01, calculate the expected 1 −year rate (E0 [r(1, 2)]), convexity and risk premium.
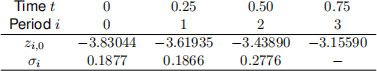
5. Suppose that you estimated the following parameters for the full Black, Derman and Toy model (1990):
(a) [25 marks] Based on the model parameters, construct the risk-neutral tree of interest rates.
(b) [25 marks] Find the 1 −year swap rate for a swap defined on the 3 − month rate with quarterly payments.
(c) [25 marks] Plot the fixed-for-floating swap value tree for the swap with the nominal value $100 and the swap rate that you found in (b). [Hint: recall that swap is determined with respect to the quarterly compounded rate.]
(d) [25 marks] Consider a European payer swaption with 6 months to maturity (i = 2), to enter at i = 2 into a 6 − month swap that you considered in (c) (i.e. the maturity of the swap is 1 year from now). Calculate the price of this swaption.
2023-07-29