IFYEC003 Economics Examination
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR
IFYEC003 Economics
Examination
Time Allowed
3 hours 40 minutes
Questions 1-22
Answer ALL questions.
These questions carry 60 marks in total.
Question 1
If wages rise in the copper industry and there is an increase in global demand for copper, what is the most likely outcome for the copper industry? [ 1 ]
A A rise in the price of copper
B A fall in the quantity of copper traded
C A fall in the price of copper
D No change in either the quantity of copper traded or the price of copper
Question 2
The diagram below shows aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply in a given economy with the original curves as AD1 and LRAS1. [ 1 ]
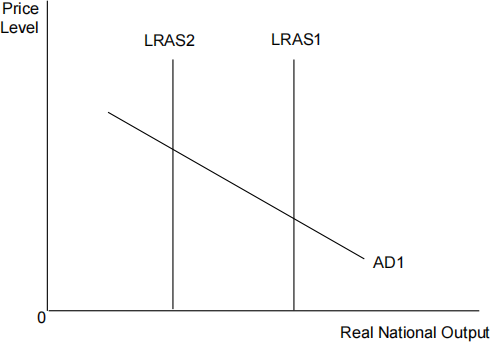
What is most likely to have caused the change in equilibrium shown?
A An increase in investment
B A fall in the value of the currency
C A fall in immigration
D A slower rate of growth of productivity
Question 3
The average of producing 10 units for a firm is £15, and the average cost 11 units is £17. What is the marginal cost of the 11th unit? [ 1 ]
A £2
B £18.50
C £37
D £187
Question 4
All other things being equal, which of the following is most likely to lead to an improvement in the balance of payments deficit of a country? A fall in [ 1 ]
A income tax rates.
B unemployment.
C the exchange rate.
D exports.
Question 5
The price of a product falls from £80 to £64 and the demand for the product rises from 300 units to 330 units. What is the price elasticity of demand? [ 1 ]
A +0.5
B -0.5
C -2.0
D -2.5
Question 6
Following the financial crises of 2008-2009, the UK experienced its worst recession in almost 50 years, and as a consequence unemployment rose quickly. The best description of the type of unemployment caused in this circumstance would be [ 1 ]
A cyclical.
B structural.
C seasonal.
D frictional.
Question 7
The diagram below shows the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves for an economy, where X is the initial equilibrium. [ 1 ]
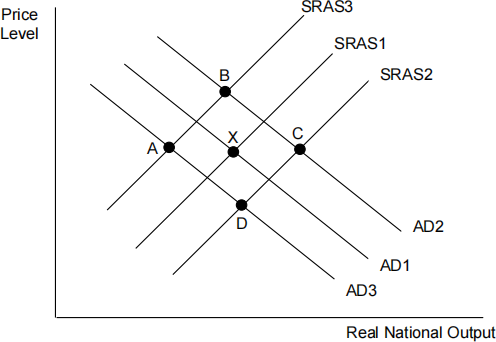
Where will be the new equilibrium position (A, B, C or D) following a significant increase in productivity and reduction in imports?
A A
B B
C C
D D
Question 8
When an increase in the rate of growth causes a correspondingly larger increase in the rate of investment this is known as [ 1 ]
A a positive output gap.
B a budget surplus.
C the multiplier.
D the accelerator.
Question 9
The diagram below shows two production possibility frontiers for a country. [ 1 ]
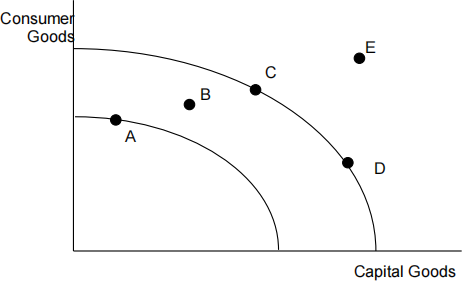
Which of the following is most likely to represent an increase in short run economic growth. A movement from
A A to C
B B to C
C C to D
D D to E
Question 10
The diagram below shows a country’s aggregate demand and supply schedules, with equilibrium at point Y. [ 1 ]
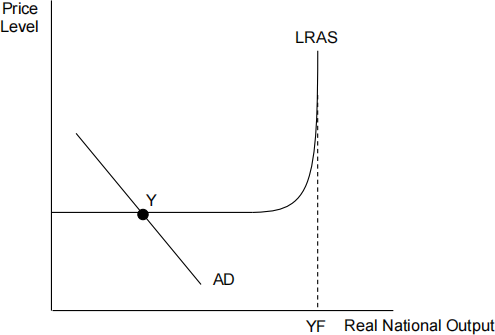
The central bank has set interest rates at 0.1% for an extended period of time, and the economy remains in equilibrium at point Y. In such
circumstances, what is the most likely policy intervention that a government might use?
A Expansionary supply side policy
B Expansionary monetary policy
C Contractionary monetary policy
D Expansionary fiscal policy
Question 11
A supermarket has estimated values of the income elasticity of demand for some of its products as shown in the table below. [ 1 ]
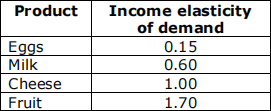
Given this information, which product is most likely to be considered a necessity?
A Eggs
B Milk
C Cheese
D Fruit
Question 12
The diagram below shows the economic cycle for a given country. [ 1 ]
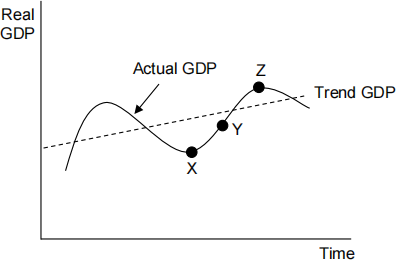
Which one of the following policies is most appropriate when the economy is at point X and wishes to move to point Y and then Z?
A Measures to strengthen the exchange rate
B Measures to constrain the money supply to combat inflation
C Contractionary fiscal policy
D Cutting interest rates
Question 13
A firm suffers from diseconomies of scale when it increases output. Which one of the following is the most likely consequence of this? [ 1 ]
A The firm must increase prices to survive
B Barriers to entry in the industry will rise
C Total production costs will fall
D The firm will reduce output
Question 14
What impact will a fall in demand for a good or service have on the supply curve? [ 1 ]
A Supply will shift to the left
B A movement down the supply curve
C Supply will shift to the right
D A movement up the supply curve
Question 15
The equilibrium market price in a competitive market of a good increases. The establishment of the new equilibrium at a higher price would most likely lead to [ 1 ]
A a rise in the demand of a complementary good.
B lower costs of production.
C new firms entering the market.
D excess demand at the new price.
Question 16
In the Phillips Curve diagram below, the economy is currently at its non- accelerating inflation rate of unemployment with an inflation rate of L. [ 1 ]
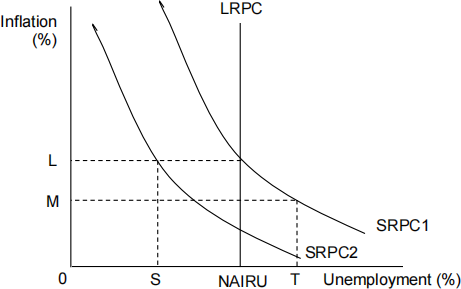
Which one of the following is least likely to reduce the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment?
A Measures to increase the mobility of labour
B Measures to improve the availability of job information
C An increase in spending on education and training
D A rise in aggregate demand
Question 17
A rise in government spending on large infrastructure projects, such as a new high speed railway line, would be most likely to [ 1 ]
A increase the budget deficit.
B increase the budget surplus.
C reduce the balance of payments deficit.
D increase the balance of payments deficit.
Question 18
At what level of output would a firm produce which has an objective of [ 1 ]
revenue maximisation?
A MR = MC
B MR = 0
C AR = AC
D AR = AFC
Question 19
In economics, the ‘ long-run’ refers to the time period when [ 1 ]
A all factors of production are fixed.
B some factors of production are fixed, others may vary.
C profit is fixed.
D all factors of production may change.
Question 20
Which one of the following applies to merit goods? [ 1 ]
A They are always provided by the government and not by the private sector
B Their marginal private benefit is less than their marginal social benefit
C They have the characteristics of non-excludability and non-rivalry.
D They cannot be supplied at a profit
Question 21:
UK petrol price jumps above £1.50 as oil costs rise
Fuel prices have hit record highs in the UK as Russia's invasion of Ukraine continues to affect global oil prices.
The average price of petrol jumped to £1.51 a litre, while diesel increased to £1.55. The cost of filling a 55-litre family car with unleaded petrol is now £83, or £85 for diesel.
The price of Brent crude oil rose by 4.6% to $102 barrel after Western nations imposed new sanctions on Russia - one the world's largest energy producers.
Petrol price movements in the UK are mainly determined by the price of crude oil, and the exchange rate between the dollar and the pound, because fuel,
like oil is traded in dollars. Petrol also has a relatively low price elasticity of demand.
UK consumers are already paying a high price for fuel, with demand surging
following the easing of Covid restrictions. Steve Irwin, from fuel consultancy
firm Portland, told the BBC that prices had also risen due to concerns over oil and gas pipelines which travel through Ukraine and carry Russian products. He said there was "potential for enormous supply disruption"
Source: The BBC [Adapted extract] – March 2022
(b) Explain using a diagram and the information in the article, why fuel [ 6 ]
prices in the UK have risen.
(c) Analyse the reasons why petrol may have a relatively low price elasticity [ 6 ]
of demand.
(d) Evaluate the extent which rising fuel prices in the economy might affect [ 6 ]
living standards.
Question 22:
UK unemployment flat as wage growth drives inflation worries
The U.K. unemployment rate remained flat at 4.1% in the last quarter of
2021 and likely declined in January, data by the Office for National Statistics showed.
The information also confirmed that fewer Britons are working than before the pandemic.
Although the number of employees on payrolls rose in January and now tops pre-pandemic levels, "the number of people in employment overall is well
below where it was before COVID- 19 hit," said ONS head of economic
statistics, Sam Beckett. "This is because there are now far fewer self-
employed people."
Around 400,000 people, mostly over the age of 50, “have disengaged from the world of work altogether and are neither working nor looking for a job,” he said, with the data pointing to an increase in long-term illness, among other factors.
Source: Politico.eu (adapted extract) – February 2022
(b) Explain using a diagram the likely effects on the UK economy if the [ 6 ]
number of people in employment overall stays below pre-pandemic levels.
(d) Evaluate the possible consequences of rising numbers of people over [ 6 ]
the age of 50 who are neither working nor looking for a job.
Questions 23 & 24
Answer 1 question ONLY
This question carries 20 marks in total.
Question 23
Explain and analyse with the use of a diagram, the likely effects of a [20]
subsidy on the market for merit goods AND evaluate the view that
subsidies are the most effective method to reduce the market failure
associated with the under provision of merit goods in society.
Question 24
Explain the different forms of mergers and acquisitions that can occur AND evaluate with the use of a diagram, the extent to which you
agree with the view that monopolistic competition will always create long term benefits to consumer welfare.
[20]
Questions 25 & 26
Answer 1 question ONLY
This question carries 20 marks in total.
Question 25
Explain and analyse the difference between direct and indirect taxation AND [20]
evaluate the view that fiscal policy is the most effective way for a
government to increase long run economic growth.
Question 26
Explain and analyse the alternative supply side policies available to a [20]
government AND evaluate the view that supply side policy is the most effective method of reducing the level of unemployment in an economy.
2023-07-26