IFYEC003 Economics
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
THE NCUK INTERNATIONAL FOUNDATION YEAR
IFYEC003 Economics
Examination
Exemplar
Time Allowed
2 hours 40 minutes
Questions 1-22
Answer ALL questions.
These questions carry 60 marks in total.
Question 1
Offering opinions within an argument is part of [ 1 ]
A microeconomics.
B macroeconomics.
C positive economics.
D normative economics.
Question 2
The diagram below shows the demand curve for tablet computers. [ 1 ]
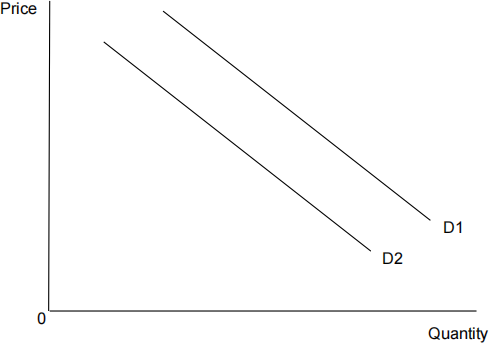
The shift of the curve from D1 to D2 would most likely have been caused by
A A fall in wages in the tablet computer industry.
B A rise in price of a good complementary to tablet computers
C A fall in the price of tablet computer components
D A rise in the price of a substitute to tablet computers
Question 3
![]() The table below shows indices of labour productivity for two firms between 2014 and 2017. [ 1 ]
The table below shows indices of labour productivity for two firms between 2014 and 2017. [ 1 ]

Which one of the following can be concluded from the data?
A Output was identical for Firm X and Firm Y in 2015
B Labour productivity fell at a faster rate in Firm X than in Firm Y between 2014 and 2017.
C Productivity in both Firms X and Y was in equilibrium in 2016
D Firm X was more profitable in 2014, but less profitable in 2017.
Question 4
Which one of the following is most likely to contribute to a decrease in the rate of inflation in an economy? [ 1 ]
A An increase in productivity
B A fall in the value of the currency
C A rise in investment
D A growing positive output gap
Question 5
A government decides to impose a maximum price on a merit good to
encourage its consumption. Which of the following is most likely to occur? [ 1 ]
A Price and quantity would be unchanged.
B Firms would expand supply to the market
C There would be excess demand.
D There would be excess supply.
Question 6
Imports in an economy are likely to decrease, all other things being equal, if [ 1 ]
A there is a fall in the exchange rate.
B there is a rise in unemployment.
C a country’s major trading partners agree to form a free trade area.
D there is a decrease in protectionist measures.
Question 7
The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves of soft drinks in the [ 1 ]
UK, where X is the initial equilibrium.
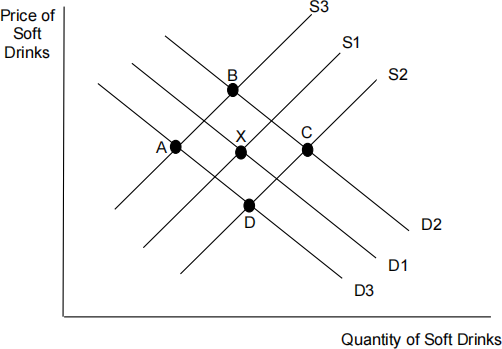
If there is a fall in the number of people drinking soft drinks following media
reports of the link between soft drinks and obesity, and at the same time,
there is a rise in productivity in the soft drinks industry, where will be the new equilibrium?
A A
B B
C C
D D
Question 8
![]() Which of the following would be expected to cause a movement along, rather than a shift of, the UK’s aggregate demand curve?
Which of the following would be expected to cause a movement along, rather than a shift of, the UK’s aggregate demand curve?
A A rise in economic growth in China
B A cut in income tax in the UK
C A rise in oil prices
D A fall in consumer confidence
Question 9
The diagram below shows the production possibility frontier private sector [ 1 ]
output and public sector output.
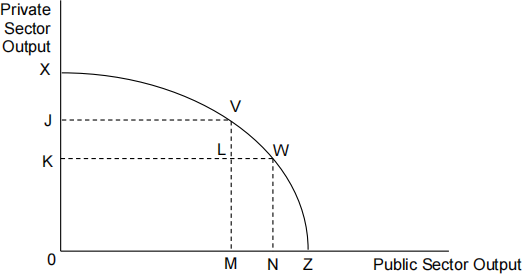
In terms of the production possibility frontier above, the opportunity cost of moving from point L to point V is
A Zero.
B MN of private sector output.
C 0B of private sector output.
D MZ of private sector output.
Question 10
The diagram below shows a country’s aggregate demand and supply [ 1 ]
schedules, with equilibrium at point X.
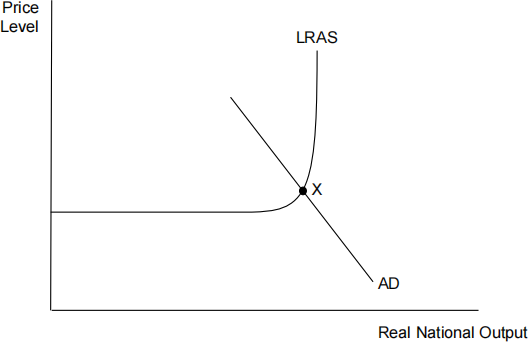
If the government now decides to pursue an expansionary monetary policy, which of the following will be most likely to occur?
A The elimination of spare capacity
B A rise in the budget deficit
C A rise in unemployment
D A fall in inflationary pressure
Question 11
![]() If there is a positive value for the cross elasticity of demand between two goods, this means that the two goods are
If there is a positive value for the cross elasticity of demand between two goods, this means that the two goods are
A complementary to each other.
B substitutes for each other.
C both inferior goods.
D unrelated to each other.
Question 12
The diagram below shows the growth rate of an economy over time. [ 1 ]
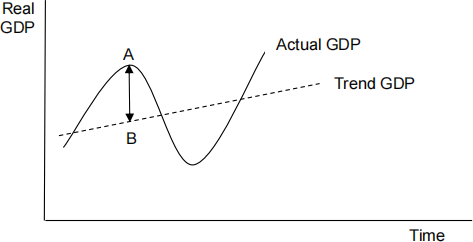
The distance AB is best described as
A the level of unemployment.
B the size of the budget surplus
C the size of the budget deficit.
D the positive output gap.
Question 13
![]() Which of the following goods or services would be least likely to be provided by the free market?
Which of the following goods or services would be least likely to be provided by the free market?
A Train travel
B Insurance
C Flood defences
D University education
Question 14
The diagram below represents the cost and revenue curves for a firm
operating as a monopoly supplier. The firm currently produces quantity Q and sells its product at a price of P. [ 1 ]
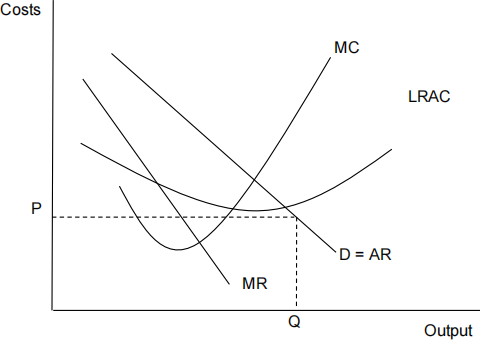
In order to increase its profits, the firm should
A produce a higher quantity and leave price unchanged.
B take no action as profits cannot be increased.
C produce a lower quantity and sell for a higher price.
D produce a higher quantity and sell for a lower price.
Question 15
Which of the following could explain why a product is price inelastic? [ 1 ]
A It is priced higher than its competitors
B There are few substitutes
C Its demand rises as incomes rise
D Buying it takes up a large proportion of somebody’s income
Question 16
![]() The diagram below shows the marginal private benefit and the marginal
The diagram below shows the marginal private benefit and the marginal
social benefit (MPB and MSB) curves and the marginal private cost and the marginal social cost (MPC and MSC) curves for education. The free market level of output is Q1 at price P1.
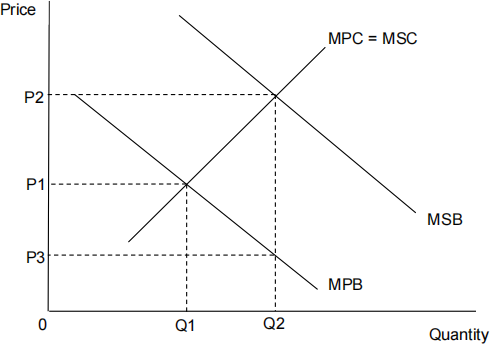
To achieve an efficient level of education, the government should
A provide a subsidy of P3-P2
B impose a minimum price of OP2.
C provide all education for free
D provide a subsidy of Q1-Q2
Question 17
![]() Other things being equal an appreciation in the value of the pound against the euro is most likely to occur if
Other things being equal an appreciation in the value of the pound against the euro is most likely to occur if
A UK imports from countries using the Euro increase
B the Bank of England allows the money supply to expand
C the UK base rate is lowered
D the number of European tourists visiting the UK increases
Question 18
Consider the table of information below showing the output of cars and [ 1 ]
bicycles in Country X and Country Y.
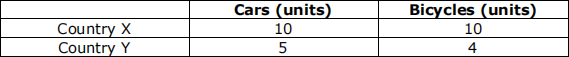
From the data, it can be concluded that
A one unit of cars has an opportunity cost of 1.25 units of bicycles in country Y
B country Y has a comparative advantage in producing cars
C country X has a comparative advantage in producing cars
D one unit of bicycles has a cost of one unit of car in country Y
Question 19
![]() Smoking cigarettes generates negative consumption externalities. This means that
Smoking cigarettes generates negative consumption externalities. This means that
A the social costs of smoking exceed the private costs of smoking.
B smoking should be banned.
C the price of cigarettes includes the external benefits of smoking.
D the social benefit from smoking is less than the private benefit from smoking.
Question 20
The diagram below shows a firm’s long run average cost curve. [ 1 ]
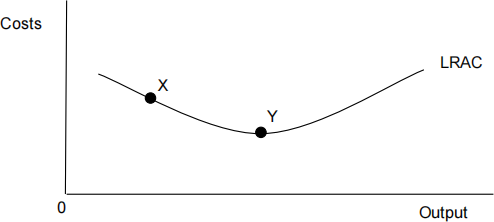
A movement from X to Y is most likely to occur because there has been
A more government regulation.
B an increase in barriers to entry.
C a worsening of available capital.
D an increase in competitiveness in the market.
Question 21
Firms admit price-fixing of concrete drainage products
Two materials firms have admitted breaking competition laws by taking part in a cartel. The Competition and Markets Authority discovered that price fixing meetings went on for seven years from in the concrete drainage sector.
Stanton Bonna Concrete Ltd and CPM Group Ltd have admitted breaking competition law by taking part in a cartel.
The products were used in large infrastructure projects across Great Britain, including water management, roads and railways.
Typical customers include engineering and construction companies; utilities providers; and local and national government.
Michael Grenfell, Executive Director of Enforcement, said: “Cartels damage competition and lead to less choice, less innovation and increased prices for customers.
“We’ve provisionally found that these three firms secretly shared out the market and colluded on prices for construction products used in many
building projects across Great Britain.
Source: www.constructionenquirer.com (adapted extract)
(a) Explain the characteristics of an oligopoly market. How and in what ways could the behaviour of the firms in the article be best explained in terms of being an example of an oligopoly market? [ 5 ]
(b) Explain with the use of a diagram why, if there is no collusion, oligopoly firms will be reluctant to compete on the basis of price. [ 5 ]
(c) Analyse with the use of a diagram why it is argued that oligopoly firms will seek to fix prices and maximise profits if successful collusion occurs. [ 4 ]
(d) Evaluate the view that “Cartels damage competition and lead to less choice, innovation and increased prices for consumers” [ 6 ]
Question 22
Inflation slows to 1.7%, removing any interest-rate
urgency for Bank of Canada
The annual rate of inflation slowed in November to 1.7% as petrol prices reduced, Statistics Canada have said.
The latest data showed the rate of inflation since the start of the year. Many experts said the inflation data reinforced predictions the Bank of Canada will
be in no rush to raise the interest rates target at its next policy announcement.
In fact, there are expectations the central bank could wait several months before its next move due to the combination of several recent economic developments.
The bank must also consider another concern — a sharp deceleration in wage growth over the past six months. The national unemployment rate has been
near a 40-year low for more than a year, but wage growth has slowed
instead of picking up its pace in the tightened labour market.
Source: www.thespec.com (adapted extract)
(a) Explain what is meant by the terms “cost-push” and “demand-pull” inflation and is there any evidence in the article that either of these are influencing the current rate of inflation. [ 6 ]
(b) Explain with the use of an aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram why lower petrol prices might have contributed to a lower rate of inflation in Canada. [ 5 ]
(c) Explain why it might be seen as surprising that despite the low level of unemployment in the Canadian economy, inflation is expected to remain low and analyse the reasons that might explain this. [ 4 ]
(d) Explain the costs of inflation in general and evaluate the extent to which inflation is a particular problem for the Canadian economy. [ 5 ]
Questions 23 & 24
Answer 1 question ONLY
This question carries 20 marks in total.
Question 23
In order to reduce the externalities of vehicles that are powered by petrol and [ 20 ]
diesel many governments have offered subsidies to manufacturers of electric vehicles which are much better for the environment. In 2021, the UK government reduced the subsidies given to producers of electric cars. Part of the reason for this is the fall in cost of the electric cars themselves over recent years and the rise in government deficits as a result of the Coronavirus pandemic and the pressure on government finances.
Analyse and explain, using appropriate diagrams, how subsidies to consumers of electric cars could correct the market failure associated with cars using petrol or diesel fuels AND evaluate the extent to which subsidies are an effective policy solution.
Question 24
Analyse, using appropriate diagrams the extent to which firms in perfect [ 20 ]
competition achieve economic efficiency in the long run. Explain carefully the features of a perfectly competitive market AND evaluate the extent to which perfect competition is a desirable market structure which always maximises society’s welfare.
Questions 25 & 26
Answer 1 question ONLY
This question carries 20 marks in total.
Question 25
Explain the different components of aggregate demand and analyse how and [ 20 ]
why consumption spending might rise. Evaluate, using appropriate diagrams the likely effects of a significant rise in consumption spending.
Question 26
![]() Explain the different types of unemployment and analyse how and why
Explain the different types of unemployment and analyse how and why
unemployment might increase in an economy. Evaluate, using diagrams
where appropriate the extent to which fiscal policy is effective in combating unemployment in an economy.
2023-07-19