QUANTITATIVE METHODS – DECEMBER 2017 Section II
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
QUANTITATIVE METHODS – DECEMBER 2017
Section II
Case Studies
Case Study 1
Every year the population of Edinburgh doubles during the month of August, when the famous Edinburgh Festival is held in venues throughout the city. It is the biggest arts festival in the world and contributes significantly to the city’s economy and cultural heritage. You have been hired as an analyst by the festival director to look at a number of different issues from last year’s festival.
Each individual show at the festival makes money through ticket sales and through the sales of paper event programmes to guests once they are in the venue. You have been asked to look at programme sales at one particular show in the Usher Hall in the city centre, which ran for 50 nights. The number of programmes sold each night was as follows:
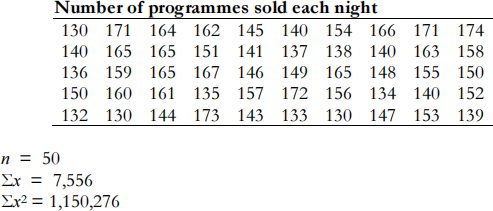
(i) Using the above data, calculate the mean, median and mode. Discuss what these statistics measure and why they have different values. (4 marks)
(ii) Find the range, the standard deviation and the quartile deviation. Describe what each of these statistics measures. (6 marks)
(iii) Construct a grouped frequency table using intervals of five units, i.e. 130–134, 135–139, 140–144, etc. (4 marks)
(iv) Use the grouped frequency table to calculate the mean. Compare this value with the one obtained in (i) above and describe why they differ. (5 marks)
(v) Write a short report on programme sales, highlighting the features of the data. Indicate any further information that should be collected. (6 marks) (Total 25 marks)
Case Study 2
During last year’s Edinburgh Festival an amateur film, which was critically acclaimed, was shown for a short run of five days at four different cinemas. The following data were collected on the number of tickets sold in each cinema as follows:
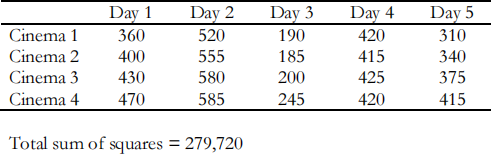
(i) Carry out a two-way analysis of variance. Produce an appropriate summary table. (10 marks)
(ii) Test whether there is a significant difference in the average number of units sold over the five days. (5 marks)
(iii) Test whether there is a significant difference in the average number of tickets sold for the four cinemas. (5 marks)
(iv) Write a short report on your findings. Indicate any other information that you consider relevant. Give recommendations for further research and analysis. (5 marks) (Total 25 marks)
Case Study 3
The director of the Edinburgh Festival wants to find out how much each international visitor to Edinburgh spent on show tickets during their stay. She was especially interested in those who spent more than £20. A survey was conducted in the city centre and the results were as follows:
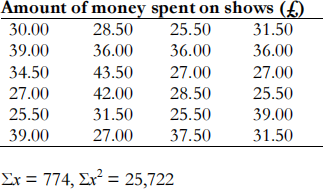
(i) Use an appropriate hypothesis test to determine whether the average amount spent is significantly greater than £20. (11 marks)
(ii) Calculate the 95% and 99% confidence limits for the average amount spent on festival tickets. (6 marks)
(iii) Write a report on your findings. Indicate any reservations you may have and the assumptions you have made. (8 marks) (Total 25 marks)
Case Study 4
The director of the Edinburgh Festival has asked you to see if there is a relationship between the level of marketing spend for a show (flyers, posters, newspaper and magazine adverts) and the number of people attending that show during its run. You have collected the following data from a random selection of 14 shows.
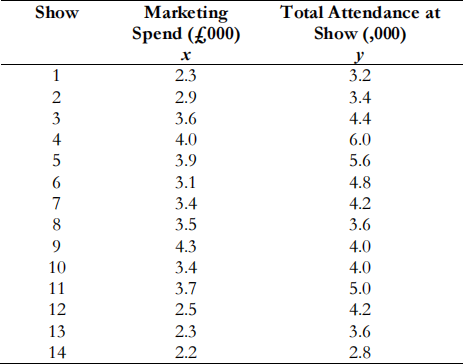
The following summary statistics have been calculated:
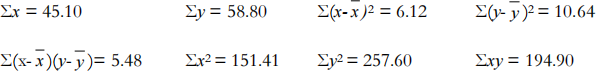
(i) Find the equation of the least squares regression line. (5 marks)
(ii) Calculate the correlation coefficient and interpret the result. (5 marks)
(iii) Calculate the R2 value and interpret the result. (4 marks)
(iv) What level of attendance would you expect to see for:
(a) An event that had a marketing spend of £3,000?
(b) An event that had a marketing spend of £6,000?
Which of the above estimates would you expect to be more accurate and why? (3 marks)
(v) Write a report on the analysis of the data. Indicate any additional information you would require and include any recommendations for further analysis. (8 marks) (Total 25 marks)
TOTAL OF 100 MARKS
2023-07-04