ECON 2012 ICB Homework 02
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON 2012 ICB
Homework 02
1. (2 point) Indicate for each of the following statements the impacts to supply and demand, “increase” or “decrease” for “supply” or “demand” .
a. “When a cold snap hits Florida (the state that produces much of the orange juice consumed in the US), the price of orange juice rises in supermarkets throughout the country.”
b. “When the weather turns warm in New England (an area in the US which experiences cold winters and warm summers) every summer, the price of hotel rooms in Caribbean resorts (on islands which are warm year-round) plummets.”
c. “When a war breaks out in the Middle East, after the price of gasoline rises, the price of a used Cadillac (a car brand famous for very large cars which have very high gasoline consumption) falls.” Describe the impact to both the gasoline market and the market for used Cadillacs.
2. (1 point) “An increase in the demand for notebooks raises the quantity of notebooks demanded at equilibrium but not the quantity supplied.” True or false?
3. (2 points ) Consider the markets for DVDs, TV screens, and tickets at movie theaters. For each pair, identify whether they are complements or substitutes:
a. DVDs and TV screens: _______________
b. DVDs and movie tickets: _______________
c. TV screens and movie tickets: _______________
d. Suppose a technological advance reduces the cost of manufacturing TV screens. How does this affect the supply and demand curves for both DVDs and movie tickets?
4. (3 points) Consider the markets for pens and pencils. Suppose that the number of students with an allergy to pencil erasers increases, causing more students to switch from pencils to pens in school. Moreover, the price of ink, an important input in pen production, has dropped considerably.
a. How are the supply and demand curves of pencils and pens affected?
b. Which direction is/are the affected curve(s) moved?
c. How does equilibrium quantity in the market for pens change? (increase, decrease or ambiguous)
d. How does equilibrium price in the market for pens change? (increase, decrease or ambiguous)
5. (1 point) The market for laptops in 2008 was in equilibrium. Then, between 2008 and 2009, the equilibrium price of laptops remained constant, but the equilibrium quantity of laptops increased.
a. From this, you can conclude that between 2008 and 2009, the supply of laptops ________ (increased, decreased, remained the same)
b. and the demand for laptops ________ (increased, decreased, remained the same)
6. (2 points) Suppose that the price of basketball tickets at your college is determined by market forces. Currently, the demand and supply schedules are as follows:
|
Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied |
||
|
4 |
10,000 |
8,000 |
|
8 |
8,000 |
8,000 |
|
12 |
6,000 |
8,000 |
|
16 |
4,000 |
8,000 |
|
20 |
2,000 |
8,000 |
a. Draw the demand and supply curves. What do we call this type of supply curve?
b. Why might this be true?
c. What are the equilibrium price and quantity of tickets?
Your college plans to increase total enrollment next year by 5,000 students. The additional students will have the following demand schedule:
|
Price Quantity Demanded |
|
|
4 |
4,000 |
|
8 |
3,000 |
|
12 |
2,000 |
|
16 |
1,000 |
|
20 |
0 |
d. Now add the old demand schedule and the demand schedule for the new students to calculate the new demand schedule for the entire college. What will be the new
equilibrium price and quantity?
|
Price |
Quantity Demanded |
Quantity Supplied |
|
4 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
7. (3 points) Market research has revealed the following information about the market for
chocolate bars: The demand schedule can be represented by the equation QD = 1,600 – 300P, where QD is the quantity demanded and P is the price. The supply schedule can be represented by the equation QS = 1,400 + 700P, where QS is the quantity supplied. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for chocolate bars. Remember that at equilibrium, quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
8. (2 points) The following graph shows two known points (X and Y) on a demand curve for tomatoes.
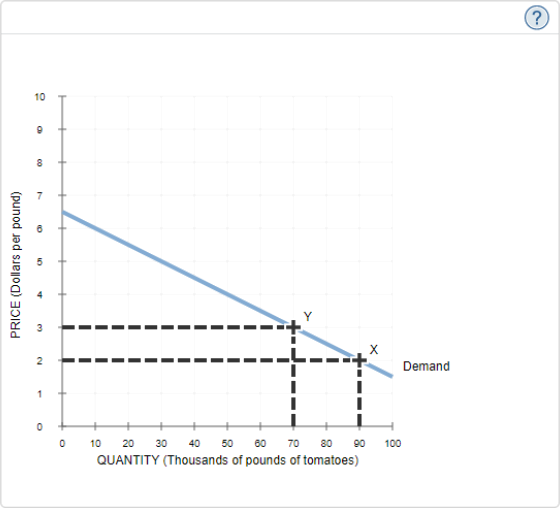
a. According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for tomatoes between point X and point Y is approximately _____.
b. This suggests that between points X and Y, the demand for tomatoes is ________ (elastic, inelastic or unit elastic)?
9. (2 points) The following graph displays four demand curves (LL, MM, NN, and OO) that intersect at point A.
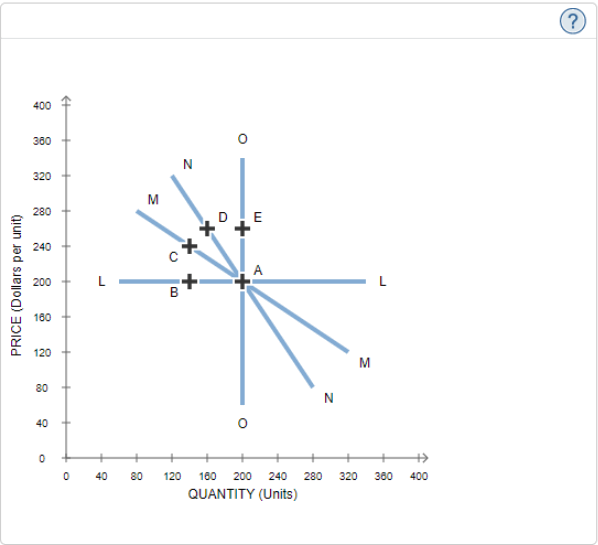
a. Between points A and C, curve MM is inelastic (True or false).
b. Between points A and B, curve LL is perfectly elastic (True or false).
c. Curve MM is less elastic between points A and C than curve NN is between points A and D (True or false).
10. (2 points) You work for a marketing firm that has just landed a contract with “Run-of- the- Mills” (this is a fictious company) to help them promote three of their products: splishy splashies, frizzles, and mookies (these names are completely made up, they are not meaningful words in English). All of these products have been on the market for some time, but to entice better sales, Run-of-the-Mills wants to try a new advertisement that will market two of the products that consumers will likely consume together. As a former economics student, you know that complements are typically consumed together while substitutes can take the place of other goods.
Run-of-the- Mills provides your marketing firm with the following data: When the price of splishy splashies increases by 5%, the quantity of frizzles sold decreases by 4% and the quantity of mookies sold increases by 5%. Your job is to use the cross-price elasticity between splishy splashies and the other goods to determine which of the goods your marketing firm should advertise together. Fill in the table below.
|
|
Cross- price Elasticity |
Complement or Substitute for Spishy Splashie? |
Advertise with Splishy Splashie (yes or no) |
|
Frizzles |
|
|
|
|
Mookies |
|
|
|
11. (1 points) For each of the following pairs of goods, which good would you expect to have more elastic demand and why?
a. required textbooks or mystery novels
b. Beethoven recordings or classical music recordings in general
c. subway rides during the next six months or subway rides during the next five years
d. root beer or water
12. (1 points) You have the following information about good X and good Y:
. Income elasticity of demand for good X = –3
. Cross-price elasticity of demand for good X with respect to the price of good Y = 2 Would an increase in income and a decrease in the price of good Y unambiguously decrease the demand for good X?
13. (2 points) The New York Times reported (Feb. 17, 1996) that subway ridership declined after a fare increase:
“There were nearly four million fewer riders in December 1995, the first full month after the price of a token increased 25 cents to $1.50 (from $1.25 to $1.50), than in the previous December, a 4.3 percent decline.”
a. Use these data to estimate the price elasticity of demand for subway rides.
b. According to your estimate, what happens to the Transit Authority’s revenue when the fare rises?
14. (2 points) Two drivers —Yang and Xiqing — each drive up to a gas station. Before looking at the price, each places an order. Yang says, “I’d like 10 gallons of gas.” Xiqing says, “I’d like $10 worth of gas.” What is each driver’s price elasticity of demand (elastic or inelastic demand)?
15. (2 points) Pharmaceutical drugs have an inelastic demand, and computers have an elastic demand. Suppose that technological advance doubles the supply of both products (that is, the quantity supplied at each price is twice what it was).
a. What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in each market?
b. Which product (drugs or computers) experiences a larger change in price?
c. Which product experiences a larger change in quantity?
d. What happens to total consumer spending on each product?
16. (2 points) A recent study found that the demand and supply schedules for Frisbees are as follows:
|
Price per Frisbee Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied |
||
|
11 |
1 million Frisbees |
15 million Frisbees |
|
10 |
2 |
12 |
|
9 |
4 |
9 |
|
8 |
6 |
6 |
|
7 |
8 |
3 |
|
6 |
10 |
1 |
a. What are the equilibrium price and quantity of Frisbees?
b. Frisbee manufacturers persuade the government that Frisbee production improves scientists’ understanding of aerodynamics and thus is important for national security. A concerned Congress votes to impose a price floor $2 above the equilibrium price. What is the new market price? (None of this actually happened.)
c. How many Frisbees are bought?
d. How many Frisbees are supplied?
e. Is this a shortage or surplus? How big is the shortage or surplus?
f. Irate college students march on Washington and demand a reduction in the price of Frisbees. An even more concerned Congress votes to repeal the price floor and impose a price ceiling $1 below the former price floor. What is the new market price?
g. How many Frisbees are bought?
h. How many Frisbees are supplied?
i. Is this a shortage or surplus? How big is the shortage or surplus?
17. (1 point) If the government places a $500 tax on luxury cars, will the price paid by consumers rise by more than $500, less than $500, or exactly $500?
18. (3 points) A subsidy is the opposite of a tax. With a $0.50 tax on the buyers of ice-cream cones, the government would collect $0.50 for each cone purchased; with a $0.50 subsidy for the buyers of ice-cream cones, the government pays buyers $0.50 for each cone purchased.
a. Show the effect of a $0.50 per cone subsidy on the demand curve for ice-cream cones, the effective price paid by consumers, the effective price received by sellers, and the quantity of cones sold.
b. Do consumers gain or lose from this policy?
c. Do producers gain or lose?
d. Does the government gain or lose?
19. (2 points) In the spring of 2008, Senators John McCain and Hillary Clinton (who were then running for president) proposed a temporary elimination of the federal gasoline tax, effective only during the summer of 2008, in order to help consumers deal with high gasoline prices.
a. During the summer, when gasoline demand is high because of vacation driving, gasoline refiners are operating near full capacity. What does this fact suggest about the price elasticity of supply (elastic or inelastic or unchanged)?
b. In light of your answer to (a), who do you predict would benefit from the temporary gas tax holiday?
2023-03-22